• AFTER THE INTERVENTION: THE OPERATING SUITES
The postoperative course can sometimes be painful the first few days, especially when implants are high-volume and especially if they are placed behind the muscles. Analgesic treatment adapted to the intensity of the pain will be prescribed for a few days. In the best case, the patient will feel a strong sense of tension.
Edema (swelling), bruising (bruises) and interferes with elevated arms are frequently the first time.
The first dressing is removed after a few days. It is then replaced with a lighter dressing. A bra can then be recommended day and night for several weeks.
Most of the time, the son of absorbable sutures are internal. Otherwise, they will be removed after a few days.
Should be considered a recovery with business interruption for a period of five to ten days.
It is advisable to wait one to two months to resume a sport.
• THE RESULT
Within two to three months is necessary to assess the final outcome. This is the time needed for the breasts have regained their flexibility and prostheses have stabilized.
The intervention has led to an improvement in the volume and shape of the breast. The scars are usually very discreet. Gain breast size has an impact on the overall silhouette, allowing greater freedom of dress. Beyond these physical improvements, the recovery of a full femininity often has a very beneficial effect on the psychological level.
. Stability result
Regardless of the life of the prosthesis (see below) and with the exception of the occurrence of a significant change in weight, breast size will remain stable in the long term. However, as regards the form and the "holding" of the chest, breasts "augmented" suffer like natural breasts, the effects of gravity and aging, with a variable speed depending on the age and supporting qualities of the skin, but also the volume of the implants.
• FAULTS OF THE RESULT
Some imperfections may occur occasionally:
. asymmetric residual volume, incompletely corrected despite implants of different sizes;
. firmness too high flexibility and mobility deemed insufficient (especially with large implants);
. a somewhat artificial, especially in very thin patients, with too much visibility of the edges of the prosthesis, especially in the upper segment;
. conspicuity touch implants is always possible, especially when the thickness of the tissue cover (skin + fat + gland) covering the prosthesis is low (a
fortiori with large implants).
In case of dissatisfaction, some of these imperfections may be eligible for surgical correction after a few months.
• OTHER MATTERS
. Pregnancy / Breastfeeding
After an introduction of breast implants, pregnancy is possible without danger, nor the patient or for the child but it is recommended to wait at least six months after surgery. Regarding breastfeeding, it is not dangerous and is possible in most cases.
. Autoimmune Diseases
The numerous international scientific work on a large scale this unanimously demonstrated that there is no more risk of developing this type of rare diseases in patients with implants (especially silicone) than in the general female population.
. Prostheses and cancer
In the current state of knowledge, we can say that breast implants, including silicone, does not increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
However, in the context of cancer screening after implantation, clinical examination and palpation may be affected especially if hull or periprosthetic siliconoma. Similarly, the presence of implants may hinder performance and interpretation of screening mammograms in regularly. It is therefore necessary to systematically identify yourself as breast implants. Thus, some specialized radiological techniques (special effects, digital images, ultrasound, MRI, etc..) May be used depending on the case. Moreover, if
doubt about the diagnosis of breast cancer, you should know that the presence of prostheses may require more invasive exploration for diagnostic certainty.
. Life implants
Although we can see some patients keep their implants decades without major changes, do not consider the implementation of breast implants as something definitive "life." Thus, A patient with implants can expect to eventually replace his dentures so that the beneficial effect is
maintained. Implants, whatever they are, have a life expectancy uncertain that it is impossible to estimate precisely because it depends on wear variable speed phenomena. The lifetime of the implants can not be guaranteed in any case.
It should be noted, however, that the new generation implants have made great progress in terms of strength and reliability. The notion of change required beyond ten years have
therefore justified with current prostheses which will be replaced when a problem is detected or justifying the opportunity to apply for aesthetic improvement of the patient (change in volume or shape, ptosis correction ...).
. Watch
It is essential to comply with the inspections prescribed by your surgeon in the weeks and months following implantation. Subsequently, the presence of implants does not relieve the usual medical supervision (gynecological care and screening for breast cancer), though it does not need to perform tests in addition to those related to such monitoring. It is necessary to specify all the various doctors involved that you are supporting breast implants.
Consultation monitoring specific to the implants, with your plastic surgeon is recommended every two to three years, but outside of this monitoring, it is especially crucial to come see if a change of one or both breasts is detected or after a violent trauma.
• POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS
. Effusions, infection
- Hematoma: blood pooling around the prosthesis is an early complication that may occur during the first few hours. If it is important, a recovery in the operating room is preferable to drain the blood and stop the bleeding at its origin;
- Serous effusion, an accumulation of lymphatic fluid around the prosthesis is a fairly common phenomenon, often associated with significant edema. It simply results in a transient increase in breast volume. It disappears spontaneously and gradually;
- Infection: uncommon after this type of surgery. It can not be solved solely by antibiotics and then require reoperation for drainage and removal of the implant for a few months (time required before replace a new prosthesis without risk).
We can also mention three other specific forms of infection:
. late infection "low noise"
it is an infection with few symptoms and no obvious translation examination, which can sometimes occur several years after implantation;
. microabscesses:
more frequent, they thrive on a stitch and resolve quickly after removal of the offending wire and wound care;
. toxic shock syndrome:
in rare cases this widespread infectious syndrome have been reported brutal.
. Skin necrosis
It is the result of a lack of tissue oxygenation due to insufficient blood supply located, which can be promoted by excessive tension, hematoma, infection and heavy smoking in the patient. It is a rare but dreaded complication because, in the extreme, it can locally to expose the prosthesis, including a dehiscence. Revision surgery is often required, sometimes the need to temporarily remove the implant.
. Abnormal healing The healing process involving fairly random phenomena, sometimes the scars are not ultimately as discreet as expected, can then take very different aspects adherent retractable extended,, hyper or hypopigmented, hypertrophic (swollen) or exceptionally keloids.
. Altered susceptibility
They are frequently the first few months but eventually most of the time by regressing. Rarely, however, a certain degree of dysesthesia (decrease or exaggerated sensitivity to touch) may persist, especially at the areola and nipple.
. Galactorrhea / effusions milk
It has been reported in very rare cases of unexplained postoperative hormonal stimulation, resulting in secretion
milk ("galactorrhea"), sometimes with a collection of fluid around the prosthesis.
. Pneumothorax
Very rare, it will benefit from a specific treatment.
. Risks specifically related to implants
. Formation of "folds" or aspect of "waves"
The implants are flexible, it is possible that their envelope folds and these folds are perceptible to the touch, even visible under the skin in certain positions, while giving an appearance of waves.
. "Cases"
The physiological constant and normal reaction of the human organism in the presence of a foreign body, is to isolate it from surrounding tissue by forming an airtight membrane that will surround the implant and is called "periprosthetic capsule." Normally, this membrane is thin, flexible and imperceptible, but sometimes the reaction is amplified and the capsule thickens, becomes fibrous and retracts compressing the implant, then taking the name of "shell". Depending on the intensity of the phenomenon, it may result in: a simple tightening of the breast, sometimes embarrassing constriction or visible deformation of the prosthesis with globulization leading to extreme hard sphere, painful, more or less eccentric. This retractile fibrosis is sometimes secondary to hematoma or infection, but most of the time its occurrence is unpredictable, resulting in random organic reactions.
Much progress has been made in recent years in terms of surgical techniques, but also design and forming implants, resulting in a substantial reduction in the rate of shells and their intensity. If necessary, reoperation may correct such contracture section of the capsule ("capsulotomy").
. Out
We have seen that the implants can not be considered definitive. A sealing of the casing may thus loss
occur over time. It may be a simple porosity of puncture openings of microcracks or outright breaches. This can be very rarely the result of a violent trauma or accidental puncture and, more often, the result of gradual wear of the surface due to seniority. In all cases, the result is a possible outcome of the product
filling of the prosthesis, with different consequences depending on the nature of the content:
. with saline or absorbable hydrogel, there is a fast or slow or partial deflating;
. with silicone gel (non-resorbable), the latter will remain contained within the membrane which isolates the prosthesis. This can then facilitate the emergence of a shell, but can also remain without consequence and go unnoticed. In some cases become much more rare (especially because of the better "cohesiveness" of current gels), however it can be a gradual penetration of the gel into the surrounding tissue. The prosthetic rupture necessary, in most cases, an intervention to change the implants.
. Malposition
Incorrect positioning or secondary displacement of implants, which can affect the shape of the breast can sometimes justify surgical correction.
. Rotation Although rare in practice the pivot prosthesis "anatomical" is theoretically possible and may affect the cosmetic result.
. Deformation of the chest wall
In rare cases, implants with capsular, long left in place, can "print" in lestissus, leaving in their removal deformation of the chest wall difficult to correct.
In total there should not overstate the risks, but just be aware that surgery, even seemingly simple, still a small share of hazards.
The use of a qualified Plastic Surgeon ensures that it has the training and skill required to avoid these complications, or effectively treat as appropriate.
These are the pieces of information that we wanted to bring you in addition to the consultation. We recommend that you keep this document, read it again after the consultation and reflect "a clear head." This reflection may raise new questions for which you wait for additional information. We are available to talk during the next consultation, or by phone, or even on the day of surgery when we meet in any way before anesthesia.
BREAST AUGMENTATION
This fact sheet was developed under the aegis of the French Society of Plastic Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery (SOF.CPRE) as an addition to your initial consultation, to try to answer all the questions you can ask yourself if you intend to make use of breast implants. The purpose of this document is to provide you with all the necessary and essential elements of information to help you make your decision with full knowledge of the facts. Also you is it advisable to read with the greatest attention.
• DEFINITION OBJECTIVES AND PRINCIPLES
Breast hypoplasia is defined by a volume of breasts underdeveloped compared to the morphology of the patient. It can be the result of insufficient development of the gland at puberty, or appear secondarily by loss of glandular volume (pregnancy, weight loss, hormonal disturbances ...).
The lack of volume can also be associated with ptosis (chest "falling" with sagging gland distension of the skin and areolas too low). The SGA is often physically and psychologically well accepted by patients who saw him as a threat to her femininity, with the consequent impairment of confidence and discomfort, sometimes deep, up to real complex. Therefore, the intervention aims to increase the volume of a breast considered too small by the implantation of prostheses.
The procedure can be practiced at any age after 18 years. A minor patient is not usually estimated able to undergo cosmetic breast augmentation.
This surgery is purely cosmetic purposes may benefit from support by health insurance.
Only a few cases of true breast agenesis (absence of any radical breast development) can sometimes expect a participation of social security prior agreement.
Breast implants currently used consist of a casing and a filling.
The envelope is always made of a silicone elastomer. However, prostheses differ in content, that is to say the filler content in the envelope.
The implant is said prefilled when the filler was incorporated in the factory (gel and / or saline). The range of different volumes is determined by the manufacturer.
Inflatable saline implants are filled by the surgeon who can adapt to a certain extent the volume of the prosthesis during surgery
• IMPLANTS prefilled SILICONE GEL NEW GENERATION
The vast majority of prostheses currently raised in France and around the world are pre-filled with silicone gel. These implants have been used for more than 40 years, have demonstrated
their safety and their excellent adaptation to this type of surgery because they are very close to the consistency of a normal breast. They have also evolved, particularly in the late 1990s to address weaknesses that could blame them. Today, all implants available in France are subject to precise and exacting standards: CE (European Community) + authorization AFSSAPS (French Agency for the Safety of Health Products). They are made of soft silicone gel surrounded by a sealed envelope, strong and elastic silicone elastomer which can be smooth or textured (rough).
The significant growth of new implants, giving them better reliability, involve both envelopes the gel itself:
. envelopes, the wall is now much stronger, prevent "sweating" of the gel to the outside (which was a major source of shells) and a wear resistance far superior;
. silicone gels "cohesive", whose consistency is less fluid, are not likely to spread in case of breakage of the envelope.
Beside the improvement of reliability, the new generation of silicone implants is also characterized by the great diversity of forms currently available, allowing a custom adaptation to each case. Thus, in addition to conventional dentures appeared round implants "anatomical" shaped profiles drop more or less high, wide or projected. This wide variety of shapes, combined with a wide range of volumes to optimize and adapt the choice, almost "tailor", prostheses according to the morphology of the patient and personal expectations.
• OTHER TYPES OF IMPLANTS
Envelopes prostheses are still silicone elastomer, the filler that differs. To date in France, only two alternatives to silicone gel are allowed:
. Saline
It is salt water (constituting 70% of the human body). These prostheses can be "pre-populated" (factory) or "air" (by the surgeon during the procedure). Because
their fluid (not gelatinous) content, they have a little natural substance, form much more "folds" perceptible to the touch or visible, and can often be victims of sudden deflation and sometimes early.
. Hydrogel
This is the latest substance having received its approval in 2005 by the AFSSAPS. It is an aqueous gel, composed largely of gelled cellulose derivative water. This gel, more natural than saline consistency is also absorbable by the body when out of the envelope.
• BEFORE THE OPERATION
Interrogation followed by a careful examination has been made by the surgeon who will take into account all the parameters that make each patient a special case (height, weight, pregnancy, suckling, thoracic morphology and breast, skin quality, importance fat and gland present, muscles ...). Depending on the anatomical context, preferences and habits of the surgeon, and the wishes of the patient, a surgical strategy has been agreed. Be predetermined and the location of scars, the type and size of implants and their positioning relative to the muscle (see below).
Preoperative blood tests should be prescribed.
The anesthetist will be seen in consultation at the latest 48 hours before the procedure.
It is sometimes useful to check the breast imaging (mammography, ultrasound). No medication containing aspirin should be taken within ten days prior to the operation.
You will probably be asked to fast (nothing to eat or drink) six hours before surgery.
• TYPE OF ANESTHESIA AND CONDITIONS OF INTERVENTION
. Type of anesthesia:
It is most often a conventional general anesthesia, in which you sleep completely.
In rare cases, anesthesia "vigil" (local anesthetic depth by tranquilizers administered intravenously) can however be used (to be discussed with the surgeon and anesthesiologist).
. Terms of admission:
The procedure usually justify hospitalization for a day. The input is then carried out in the morning (or sometimes the day before in the afternoon) and the output is allowed the following day. However, in some cases, the procedure can be done in "ambulatory", that is to say with out the same day after a few hours of monitoring.
• INTERVENTION
Each surgeon adopts a technique of its own and it adapts to each case to obtain the best results. However, it may hold common basic principles:
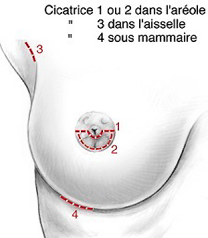
. Skin incisions
There are several "first tracks" possible:
. aerial pathways, with incision in the lower segment of the circumference of the areola, or horizontal opening bypassing From underneath the nipple (1 and 2);
. axillary, with incision under the arm, in the armpit (3);
. subcutaneous breast, with incision placed in the groove located under the breast (4).
The layout of these incisions is of course the location of future scars, which will therefore be concealed in junction zones or natural folds.
. Placing implants
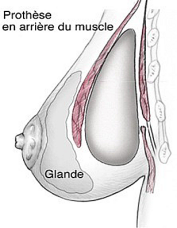
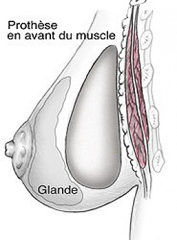
Through the incisions, implants can then be introduced to the lodge previously performed. Two positions are available:
. prémusculaire where implants are placed directly behind the gland in front of the pectoral muscles;
. retromuscular where implants are placed deeper, behind the pectoral muscles.
The choice between these two locations, with their respective advantages and disadvantages will be discussed with your surgeon.
. Complementary Care
In cases of breast ptosis associated (sagging breasts, areolas low), we saw that it might be desirable to reduce the skin envelope in order to make it back ("mastopexy"). This resection of skin then result in larger scars (around the areola ± vertical).
. Drains and dressing
A small drain may be implemented depending on the surgeon's habits. It is a device for removing blood that may accumulate around dentures.
After surgery, a dressing "modeling" is made with an elastic bandage.
Depending on the surgeon, the surgical approach and the possible need for additional procedures associated intervention can last 1:00 to 2:30.



AESTHETIC PLASTIC
& RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY

© Docteur Garson MAJ 2013